-
Tensorflow에서 사용하는 데이터 배열 Tensor 사용하기(constant, Variable)Data Science/Tensorflow 2022. 10. 24. 22:12반응형
Numpy에서 Numpy.array를 사용하듯이 Tensorflow에서는 tensor를 사용한다.
본 포스팅에서는 Tensor란 무엇이고, Tensor를 어떻게 다룰수 있는지 알아본다.
1. Tensorflow.constant
contant tensor는 생성후 값의 수정이 불가능한 Tensor이다.
1.1 Constant tensor 생성
tensor = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5])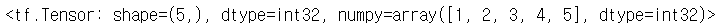
생성되는 tensor의 데이터 타입을 지정해줄 수도 있다.
tensor = tf.constant([1,2,3], dtype='float32')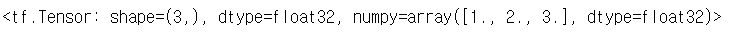
1.2 Constant tensor 정보 확인
생성된 tensor로부터 아래의 정보를 얻을수 있다.
tensor = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5]) print(tensor.shape) # 생성된 Tensor가 가지는 차원정보 #=> (5, ) # (5, )는 (5,1)과 같은 의미이다 print(tensor.dtype) # 생성된 Tensor가 가지는 데이터 타입 #=> <dtype: 'int32'> print(tf.size(tensor)) # 생성된 Tensor가 가지는 데이터 수 #=> tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32) print(tf.rank(tensor)) # 생성된 Tensor가 가지는 차수 #=> tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)단순한 1차원이 아닌 3차원의 Tensor의 경우를 확인해보자.
tensor = tf.constant([[[1,1,1,1],[2,1,2,3]],[[1,7,8,9],[1,11,22,33]]]) print("shape:", tensor.shape) print("type:", tensor.dtype) print("size:", tf.size(tensor)) print("rank:", tf.rank(tensor))
2. Tensorflow.Variable
Variable tensor는 수정 가능한 Tensor이다.
2.1 Variable tensor 생성
var = tf.Variable([0,0,0], dtype = 'float32')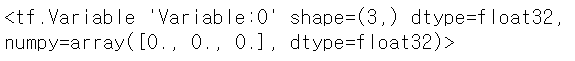
2.2 Variable tensor 값 변경 및 더하기
var.assign([1,2,3])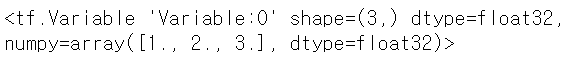
var.assign_add([1,1,1])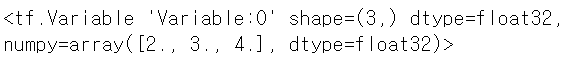
2.3 Variable tensor 정보확인
constant tensor와 동일하며, 아래와 같다.
print("shape:", var.shape) print("type:", var.dtype) print("size:", tf.size(var)) print("rank:", tf.rank(var))
3. Reshape
reshape 명령어를 사용해서 tensor의 차원정보를 변환할 수 있다.
단, 변환하는 차원정보가 기존의 차원에서 변환 가능해야한다.
(필요한 총 데이터수가 같아야 한다.)
tensor = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5,6]) print(tensor)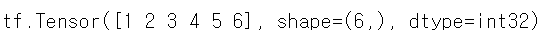
# tf.reshape(변환할tensor, 변환할 차원정보) tf.reshape(tensor,[3,2])
numpy나 pandas와 마찬가지로 -1을 사용할수 있다.
tf.reshape(tensor,[3,-1]) # [3,2] == [3,-1] == [-1,2] 모두 같은 의미
4. Tensor 연산
4.1 더하기 & 곱하기
tensor2d = tf.constant([1,2,3]) # 더하기 tensor2d + tensor2d #=> [2, 4, 6] # 텐서형식 생략 # 곱하기 5 * tensor2d #=> [5, 10, 15] # 텐서형식 생략4.2 전치(Transepose)
tensor2d = tf.constant([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) tf.transpose(tensor2d)
4.3 행렬곱(Matrix Multiplication)
x = tf.constant([[1,2]]) tensor2d = tf.constant([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) tf.matmul(x, tensor2d) #=> [[ 9, 12, 15]] # 텐서형식 생략4.4 총합 및 평균(Sum / Mean)
tensor2d = tf.constant([[1.0, 2.0],[3.0, 4.0]]) my_sum = tf.reduce_sum(tensor2d) print(my_num) #=> tf.Tensor(10.0, shape=(), dtype=float32) my_mean = tf.reduce_mean(tensor2d) print(my_mean) #=> tf.Tensor(2.5, shape=(), dtype=float32)4.5 차원 추가
tensor2d = tf.constant([1,2,3]) tf.expand_dims(tensor2d,1)
5. Random Tensor 생성
#tf.random.uniform( 차원정보, maxval=최대값, minval=최소값, dtype=데이터타입 ) #모든 숫자를 동일한 확률로 생성 random_tensor1 = tf.random.uniform([10], maxval=5, dtype=tf.int32) #tf.random.normal( 차원정보, 평균, 표준편차 ) #정규분포에서 임의의값 생성 random_tensor2 = tf.random.normal([10], 10, 1) print(random_tensor1) print(random_tensor2)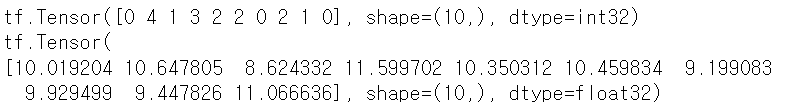
6. Data Type Casting
Tensor의 데이터타입을 변경할때는 casting을 사용한다.
tensor = tf.constant([1,2,3]) tensor_cast = tf.cast(tensor,tf.float32) print(tensor_cast) 반응형
반응형'Data Science > Tensorflow' 카테고리의 다른 글
Tensorflow 최적화 함수 종류(Optimization Function, tf.keras.optimizers) -작성중- (0) 2022.10.26 Tensorflow Convolution Neural Network 예시 코드(CNN, MNIST DataSet) (0) 2022.10.26 Tensorflow Multilayer Perceptron 예시 코드(MLP, MNIST DataSet) (0) 2022.10.24 Tensorflow 세팅 확인(버전확인, GPU확인, GPU 지정, 지정된 GPU 확인) (0) 2022.10.24 Tensorflow 기초 목록 (0) 2022.10.24